Plant vs Animal Cell – Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell
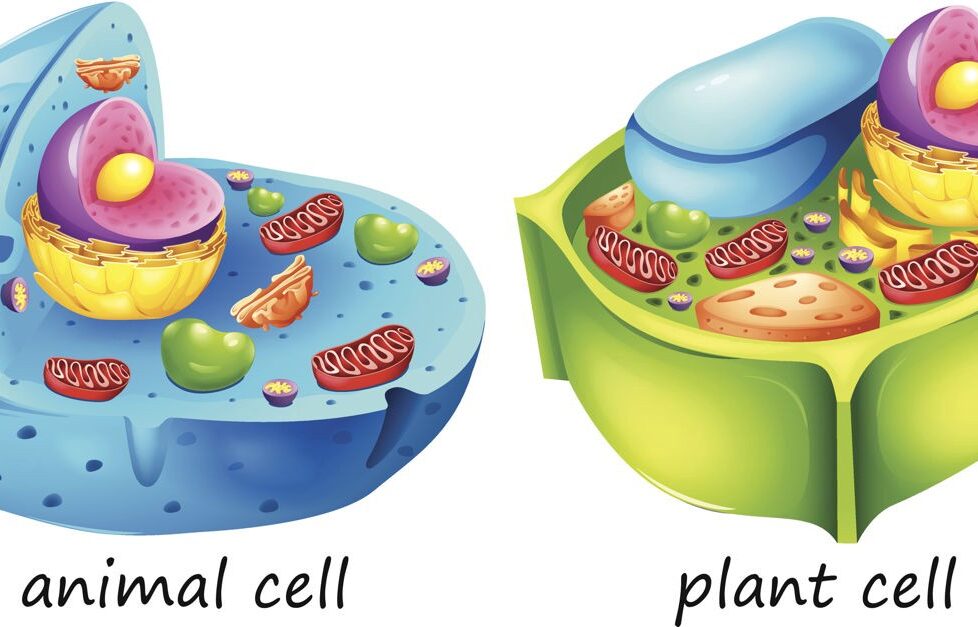

The cell is the most fundamental unit of the existence of living organisms. All life activities are carried out by cells, and the cell is the lowermost unit required for independent existence. Consequently, organisms are classified based on the number, structure, and organization of cells.
In any given ecosystem, plants are the produces and animals, consumers. Do you think the structures of their cells are different? If you do, you’re right.
Most of the differences are set on cell organelles. While most organelles are common to both plant and animal cells, some of them are unique to a particular one. Their similarities are because they both share the status of “eukaryotes” or organisms with an advanced cell type.
The following are the major differences between plant and animal cells.
| Characteristics | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| Shape | Plant cells are square or rectangular. | Animal cells are usually round or circular. |
| Cell wall | Outside the cell membrane, a presence of a protective layer known as the cell wall is present. | The cell wall is absent in animal cells. |
| Nucleus | Here, the nucleus is placed at the side because it is pushed away by a large vacuole. | Here, the nucleus is located centrally. |
| Lysosomes (also called suicide bags of the cell) | They are rarely present. | They are present in full measure. |
| Centrosomes | They are absent here. | They are present here. |
| Plastids | These are mainly responsible for photosynthesis and are hence present in the plant cell. | Absent.
|
| Vacuoles | Multiple large or a single large vacuole that is placed centrally. | Numerous amounts of vacuoles present that are usually very small. These are scattered across the cell. |
| Cilia | Absent. Plant cells are non-motile. | Most animal cells contain cilia in abundance. |
| Mitochondria (also called powerhouses of the cell) | Present but are rather few in number. | Present in abundance. |
| Mode of Nutrition | They are primarily autotrophic, with few exceptions. | They are heterotrophic without any known exceptions. |
| Size | Usually between 10-30 micrometers. | Usually between 10-100 micrometers. |
These are present in plants and algae but not in animals. These organelles are responsible for the process of photosynthesis which happens with the help of nutrients and sunlight. As autotrophs, they create their food, and all heterotrophs are directly or indirectly dependant on them.
Chloroplasts have their DNA and are believed to have been a type of prokaryotic bacteria housed in algae about 1.5 billion years ago which was then modified to become organelles.
A vacuole is an organelle that holds substances called the cell sap. The vacuole is usually a large one in plants and many small ones in animals. In animals, it has a second function of providing rigidity through pressure.
They are present only in plant cells. This is because they are non-motile and need protection from external conditions, and that is where the cell wall comes into play. It provides rigidity and protection to the cell and fixates its cytoplasm. It also protects the cell from bursting due to the turgor pressure applied by the vacuole. It is mainly composed of cellulose.


The main similarity between the plant and animal cells is that they are both eukaryotes. Moreover, they are all part of the domain Eukarya because they have a well-defined nucleus with a proper nuclear membrane and other membrane-bound organelles.
Another similarity is that cell division occurs through meiosis and mitosis and not binary fission.
When it comes to organelles, they both have a well-defined nucleus.
Also, they both have the endoplasmic reticulum, which is responsible for protein synthesis, among other things.
They also both contain mitochondria, although plants have them in fewer numbers. The function is the production of energy for the metabolic activities of the cell.
Golgi apparatus packages all the proteins produced by the ER. They are present in both plant and animal cells.
They also both contain ribosomes and the cytoplasm, which is the site of all living cell activity.
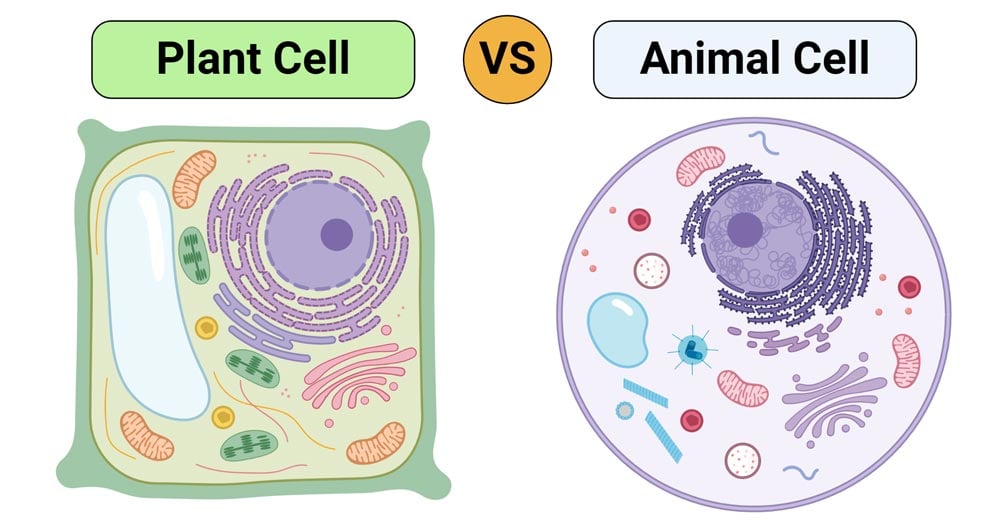

The function of the plant cell is really simple. Plant cells are the building blocks of plants, and their major function is photosynthesis, without the existence of which, heterotrophs would cease to exist.
Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts. It is the process of food preparation through the absorption of minerals, sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. Energy in the form of ATP is formed in this process.
There are many types of plant cells, primarily:
Animal cells are the fundamental units of an animal body. Majorly, they support the structure, form, internal and external activities, transportation, and more in the body.
There are admittedly numerous types of cells. The most common of them are given below.
Cells are the basic unit of life, and they differ in shapes, sizes, and functions. However, plant cells and animal cells have some common features, mainly because they are eukaryotic. The reason they differ is that animals are usually locomotive and plants are stationary.
So, plants need protection, and animals need motility. Another reason is the fact that plants are autotrophs and animals, heterotrophs. So, plants need to produce their food while animals simply need to acquire the produced food.